The year was 2017, and the astronomers of this planet observed an interstellar object that resembled the shape of a cigar. The object in question, known as Oumuamua, made an appearance in our solar system and was visible to the human eye for a mere four months before vanishing into the unknown, and it is widely believed that it exited our star system. Ever since that momentous sighting, the scientists on this planet have been racking their brains in an attempt to understand the forces behind the object’s peculiar acceleration and the truth behind its origins.
Accordingly, a study was recently conducted in an attempt to demystify the object that has caused such bewilderment among the scientific community. The study concluded that Oumuamua was, in fact, not an alien spacecraft but, rather, a natural interstellar visitor that journeyed to our solar system from another star system. While many had postulated that the object might be of an extraterrestrial origin, the researchers responsible for the study concluded that it was a natural phenomenon.
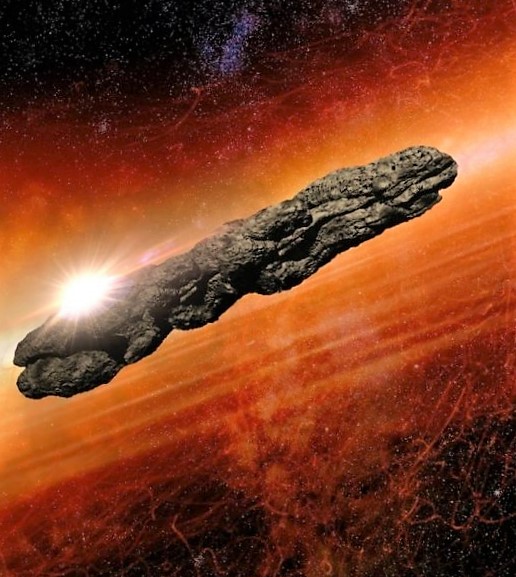

One of the most intriguing questions surrounding Oumuamua’s arrival in our solar system was the curious acceleration that the object exhibited as it moved away from the Sun. Although scientists initially thought that it was a comet, its trajectory was more akin to that of an asteroid, raising questions about its origin and behavior.
The researchers behind the study believe that Oumuamua was a rock that was once a part of a planetesimal, a celestial object similar to a small planet, that collided with another object before breaking away and embarking on its long journey through space. The scientists further suggest that hydrogen was responsible for the object’s acceleration during its departure from the Sun. The Sun’s heat caused the hydrogen molecules that were trapped in the ice below the surface of the space rock to be ejected into space, thus causing the object to move in an unusual way.
It is worth noting that no hydrogen gas emissions were observed by the scientists studying Oumuamua. However, they believe that as the object approached the Sun, more ice melted, which resulted in more gas being released, causing the object to move even faster. Although the theory of hydrogen gas emissions being responsible for the changes in Oumuamua’s trajectory is still just a hypothesis, the scientists admit that further observations of similar objects are needed to confirm their theory. Nevertheless, they stress that there is no evidence that Oumuamua is related to extraterrestrial life.
The scientific community has been trying to make sense of Oumuamua’s trajectory, shape, and composition ever since its arrival in our solar system back in 2017. One of the most significant issues that have left the scientists scratching their heads is how the object was accelerating as it moved away from the Sun. Despite initial beliefs that it was a comet, the object’s trajectory was more in line with that of an asteroid.
Scientists now hypothesize that hydrogen gas emissions were responsible for the changes in Oumuamua’s trajectory, given that the object likely contained enough hydrogen to make such a claim feasible. As Oumuamua traversed through interstellar space, the cosmic radiation could have melted the water ice, resulting in the release of the hydrogen gas. However, the scientists admit that further observations of similar objects are necessary to confirm their hypothesis. Nevertheless, they remain adamant that there is no connection between Oumuamua and extraterrestrial life.
In conclusion, the study has shed light on the interstellar object Oumuamua, revealing that it is a natural object and not an alien spacecraft. The object’s strange acceleration can be attributed to the ejection of gaseous hydrogen during its departure from the Sun. The researchers believe that Oumuamua’s origin is a rock that broke off a planet esimal after colliding with another similar object, setting off on a voyage into the distant reaches of space. The hypothesis of hydrogen gas emissions being responsible for the changes in Oumuamua’s trajectory is still in need of confirmation through further observations of similar objects. However, the findings from the study present a fascinating opportunity to expand our knowledge and understanding of the universe.
The discovery of Oumuamua has opened a new chapter in the study of interstellar objects, one that has brought scientists one step closer to unraveling the mysteries that lie within. With continued research and exploration, we can hope to gain greater insight into the workings of the universe and the celestial objects that call it home.
Google News | Telegram