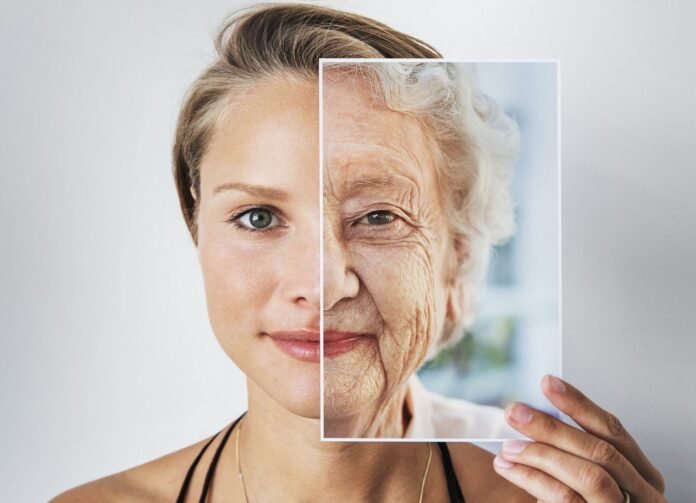
Aging is a universal process that affects all living organisms. While it is an inevitable part of life, recent developments in anti-aging research have shown that we may be able to slow down the aging process and extend the healthy years of our lives. In this article, we will delve into the latest discoveries in the science of aging, including the role of genetics, lifestyle factors, emerging therapies, nutraceuticals, and personalized medicine.
The Role of Genetics
Research has demonstrated that genetics plays a significant role in the aging process. Our genes determine our susceptibility to age-related diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and cardiovascular disease. Scientists are currently studying the genes associated with aging to comprehend how they function and how they can be manipulated to slow down the aging process.
The SIRT1 gene, for example, is involved in regulating cell metabolism and DNA repair. Activating this gene has been shown to extend the lifespan of various organisms, including mice and roundworms. Researchers are currently investigating the potential of SIRT1 activators as anti-aging therapies for humans.
Lifestyle Factors
While genetics plays a significant role in aging, lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise also have a major impact on the aging process. A healthy diet, rich in fruits and vegetables, can provide the body with the nutrients it needs to repair and maintain cells, while regular exercise can help to maintain muscle mass and reduce the risk of age-related diseases.
Other lifestyle factors that have been shown to impact aging include sleep quality, stress levels, and social connections. Getting enough sleep, managing stress, and maintaining strong social connections can all help to promote overall health and well-being, and may contribute to a longer and healthier life.
Emerging Therapies
In addition to genetics and lifestyle factors, researchers are also exploring new therapies to slow down the aging process. One promising area of research is the use of senolytic drugs, which target and destroy senescent cells – cells that have stopped dividing and are thought to contribute to aging and age-related diseases.
Other emerging therapies include stem cell therapy, which involves using stem cells to repair damaged tissues and organs, and gene therapy, which involves manipulating genes to correct genetic mutations that contribute to aging and age-related diseases.
Nutraceuticals
Nutraceuticals are supplements that are derived from natural sources and have potential health benefits. These supplements have gained popularity in recent years, and many have been shown to have anti-aging properties.
Resveratrol, a compound found in red wine and grapes, is an example of a nutraceutical with anti-aging properties. Resveratrol has been shown to activate the SIRT1 gene, which can help to protect against age-related diseases and extend lifespan. Another nutraceutical with anti-aging properties is NAD+, a coenzyme that plays a key role in cell metabolism and DNA repair. NAD+ levels decline with age, and supplementing with NAD+ precursors has been shown to improve overall health and extend lifespan in animal studies.
Personalized Medicine
As our understanding of the genetics and biology of aging continues to grow, personalized medicine is becoming an increasingly important area of research. Personalized medicine involves tailoring treatments to an individual’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle factors, and health history.
By taking a personalized approach to anti-aging research and therapy, scientists can develop treatments that are more effective and less likely to cause adverse side effects. This approach could also help to identify individuals who are at higher risk for age-related diseases, allowing for earlier intervention and treatment.
In Conclusion
In conclusion, recent discoveries in anti-aging research have shown that we may be able to slow down the aging process and extend the healthy years
of our lives. However, it is important to note that the science of aging is complex and multi-faceted, and there is still much that we do not understand about the aging process. While promising therapies and treatments are being developed, it is important to approach anti-aging research with caution and skepticism, and to ensure that any treatments are thoroughly tested for safety and efficacy before being made widely available.
Ultimately, the goal of anti-aging research is not to find a cure for aging, but rather to extend the healthy and productive years of our lives. By continuing to explore the science of aging, we can better understand the factors that contribute to aging and age-related diseases, and develop new strategies for promoting healthy aging and reducing the risk of age-related illnesses.
In conclusion, the quest to slow down the aging process is a complex and challenging one, but recent developments in anti-aging research have given us new insights and opportunities for developing innovative treatments and interventions that could help to extend lifespan and improve overall health and well-being. The future of anti-aging research is bright, and we can look forward to continued advancements in the field as we strive to unlock the secrets of healthy aging.
Google News | Telegram