The growth of air pollution has become an increasingly intricate challenge, posing an enormous threat to the well-being and health of humans, animals, and the environment. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), around seven million premature deaths are caused annually by polluted air, with nine out of ten individuals breathing it in. While human activities are responsible for contributing to air pollution, technology has emerged as a highly promising solution to mitigate it. In this article, we shall delve into the multifaceted ways technology can reduce air pollution.
What is Air Pollution?
Air pollution constitutes the presence of deleterious substances in the air that we inhale, such as gases, particles, and biological molecules that may cause harm to human health, animals, and the environment. Carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, ozone, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are among the most common air pollutants.
Health Effects of Air Pollution
Exposure to air pollution has severe health implications, causing respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, stroke, and cancer. Prolonged exposure to air pollution can also affect the immune and nervous systems. The elderly, children, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions are especially vulnerable to the detrimental effects of air pollution. Furthermore, air pollution has far-reaching environmental consequences, damaging crops, forests, and other vegetation, reducing biodiversity, and contributing to climate change.
Renewable Energy
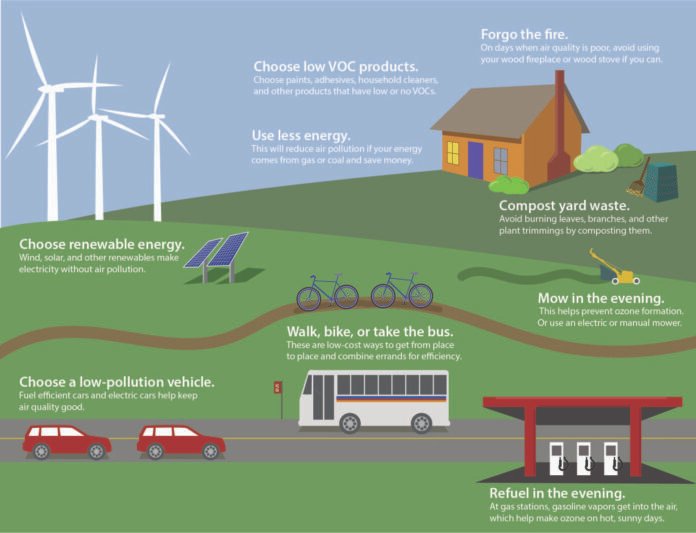
The burning of fossil fuels for energy is a significant contributor to air pollution. However, renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydropower do not emit any harmful pollutants, making them an excellent alternative. Advances in technology have made renewable energy sources more accessible and cost-effective, thus considerably reducing the amount of air pollution generated by the energy sector.
Electric Vehicles
Motor vehicles are a substantial source of air pollution, particularly in urban areas. Electric vehicles (EVs) provide a cleaner alternative to conventional vehicles. EVs utilize electric motors powered by batteries or fuel cells, thereby eliminating tailpipe emissions. Advances in battery technology and the production of renewable electricity have made the development of EVs possible.
Air Quality Monitoring
Air quality monitoring is vital in the fight against air pollution. Advancements in technology have made air quality monitoring more precise and accessible. Low-cost sensors can now measure air pollution in real-time, enabling more timely and effective interventions. Data obtained from air quality monitoring can also be used to develop air pollution control policies.
Clean Energy Technologies
Clean energy technologies are highly beneficial as they do not emit harmful pollutants into the air. Advances in clean energy technologies have made them more affordable and accessible, thereby reducing the amount of air pollution generated by the energy sector. Clean energy technologies can also be used in various industries such as transportation, agriculture, and construction to reduce their environmental footprint.
Air Pollution Control Technologies
Air pollution control technologies are designed to reduce the emissions of harmful pollutants from various sources. Scrubbers, catalytic converters, particulate control, and flue gas desulfurization are among the technologies used to reduce the emissions of harmful pollutants from power plants, factories, and transportation.
Smart Cities
Smart cities use technology to enhance the quality of life of their residents, including air quality. Air quality sensors, traffic management systems, and public transportation systems are technologies used by smart cities to monitor and control air pollution. Smart cities also employ data analytics to identify the sources of air pollution and develop targeted interventions.
Carbon Capture and Storage
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) capture carbon dioxide emissions from various sources and store them underground or in other storage facilities. CCS can be used in industries such as power plants, factories, and transportation. The technology can significantly reduce the amount of carbon dioxide emissions generated by various sources.
Conclusion
Air pollution poses a significant threat to human health, the environment, and biodiversity. Technology has emerged as a promising solution to mitigate air pollution. Advances in renewable energy, electric vehicles, air quality monitoring, clean energy technologies, air pollution control technologies, smart cities, and carbon capture and storage have all contributed to reducing air pollution. However, the adoption of these technologies requires a collaborative effort between governments, industries, and individuals. Policies and regulations that encourage the adoption of clean technologies are necessary to reduce air pollution.
Individuals can also play their part by adopting sustainable lifestyles and supporting clean technologies. This can be achieved through reducing energy consumption, using public transportation, and investing in renewable energy. With a concerted effort, technology can play a significant role in reducing air pollution and creating a healthier environment for all.
Google News | Telegram