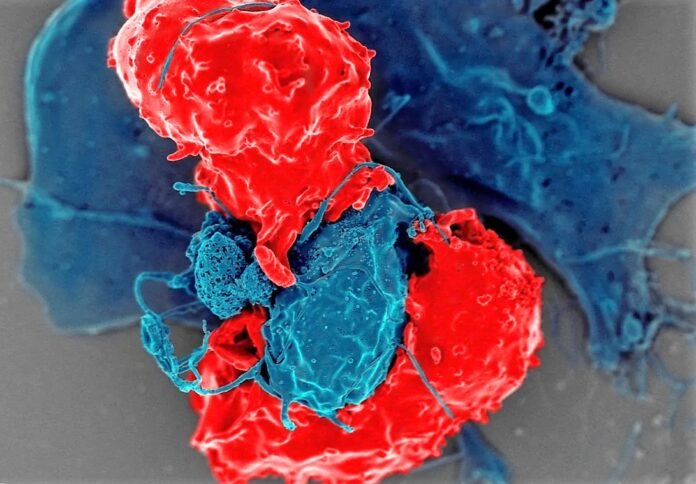
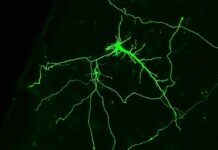
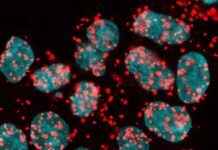
It’s no secret that gut microbes impact our overall well-being, but recent findings published in Immunity now suggest an even more significant role in tissue regeneration. The study reveals how these microscopic organisms orchestrate immune responses, mitigate inflammation, and encourage the wound healing process. Central to this performance are regulatory T cells – immune system’s “peacekeepers” – which facilitate healing in mice muscles. Surprisingly, without gut bacteria, inflammation could stand in the way of recovery, potentially causing fibrosis.
Peering into the Microscopic World: Study Insights
Delving into the crux of the matter, the researchers discovered that colon-residing regulatory T cells in mice hold the key to tissue regeneration. Intriguingly, gut microbes were found to be indispensable in this process. Optical tagging, a technique employed to monitor cellular movements, revealed that these cells journeyed from the gut to muscles and other organs. Furthermore, the presence of identical T cell populations in the gut and muscle tissue of healing mice strengthened the hypothesis that regulatory T cells indeed traversed from the gut to the muscle, contributing to the healing process.
Revealing Findings: The Role of RORγ+ Regulatory T Cells
In the absence of RORγ+ regulatory T cells, genetically engineered mice exhibited delayed healing and fibrosis development, emphasizing the importance of these cells in muscle repair. Interestingly, the administration of antibiotics and exposure to germ-free environments inhibited healing in mice, as gut microbes were found to activate the essential regulatory T cells involved in the healing process.
Food for Thought: Antibiotics and Wound Healing
This groundbreaking study raises eyebrows regarding the use of antibiotics in tissue injury scenarios, as colon regulatory T cells rely heavily on gut bacteria. Researchers urge caution when prescribing antibiotics, particularly for patients who have recently undergone surgery or those with severe wounds, as these individuals often receive antibiotic treatment. Furthermore, the potential involvement of gut microbes in other inflammatory disorders – such as autoimmune diseases and increased tumorigenesis – warrants attention, given the association between the inflammatory cytokine IL-17 and these conditions.
A Conclusive Note: The Symbiotic Relationship
Providing compelling evidence for the pivotal role gut microbes play in wound healing and tissue regeneration, this study accentuates the significance of regulatory T cells and maintaining a healthy microbiome for proper healing. Future research endeavors may investigate the impact of gut microbes on other inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, potentially unveiling novel treatment strategies and preventative measures.
Further Implications and Future Directions
As the understanding of the complex relationship between gut microbes, immune system, and tissue regeneration expands, it could reshape the landscape of medical treatment and healthcare practices. This newfound knowledge may lead to the development of innovative therapies that harness the power of the microbiome to facilitate wound healing and tissue repair in patients. Moreover, it may inspire a reevaluation of current practices surrounding antibiotic prescription and administration.
Microbiome-based Therapies and Personalized Medicine
With the emerging knowledge of the integral role of gut microbes in wound healing, researchers may explore microbiome-based therapies to enhance tissue regeneration. Probiotics, prebiotics, and fecal microbiota transplants could potentially be used to modulate the microbiome, aiding in the healing process. In the long run, personalized medicine approaches that consider individual microbiome profiles may be designed to optimize patient recovery and overall health.
Challenges and Limitations
While the study offers valuable insights, it’s crucial to acknowledge the limitations and challenges that lie ahead. Translating the findings from mice to humans may prove to be complex, as differences in anatomy, physiology, and microbiomes between species could impact the results. Additionally, a deeper understanding of the precise mechanisms through which gut microbes interact with the immune system to facilitate tissue regeneration is required.
Collaborative Research and Multidisciplinary Approaches
Unraveling the intricate connections between gut microbes, immune system, and tissue regeneration necessitates a collaborative approach, drawing from various fields such as immunology, microbiology, and regenerative medicine. By combining knowledge and expertise from these disciplines, researchers can overcome challenges and limitations, paving the way for breakthrough discoveries that could transform patient care and recovery.
A New Era of Healing: Embracing the Microscopic Allies
As we continue to uncover the mysteries surrounding gut microbes and their influence on the immune system and tissue regeneration, we are reminded of the importance of maintaining a healthy, balanced microbiome. Embracing these microscopic allies and understanding their role in our well-being could usher in a new era of healing, where the power of our gut is harnessed to enhance recovery and improve overall health.
Public Awareness and Education
As the scientific community delves deeper into the relationship between gut microbes, the immune system, and tissue regeneration, it is crucial to raise public awareness and disseminate this knowledge. Educating the general public about the importance of a healthy microbiome and its potential impact on wound healing, tissue repair, and overall health can lead to better lifestyle choices and informed decisions regarding antibiotic usage.
Integrating Microbiome Health into Daily Life
Simple lifestyle changes, such as incorporating a diverse diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods, can promote a well-balanced gut microbiome. In addition, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep can positively influence gut health. By integrating these habits into daily routines, individuals can support their microbiome and, consequently, enhance their overall well-being and recovery capabilities.
Regulatory Considerations and Ethical Implications
As research advances in the field of gut microbiome and its impact on tissue regeneration, regulatory bodies and policymakers will need to assess the potential implications of these findings. This may involve revisiting current guidelines on antibiotic prescriptions, reevaluating the use of antibiotics in agriculture, and promoting public health initiatives that emphasize the importance of a healthy microbiome.
Ethical Concerns: Balancing Benefits and Risks
Future microbiome-based therapies and personalized medicine approaches will likely raise ethical concerns, such as privacy issues related to genetic data and potential inequalities in access to these novel treatments. As such, it is crucial for researchers, clinicians, and policymakers to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and address ethical concerns in a transparent and responsible manner.
Embracing a Holistic Approach to Health and Healing
The insights gained from studying the complex interplay between gut microbes, the immune system, and tissue regeneration underscore the importance of adopting a holistic approach to health and healing. By considering the intricate connections between various bodily systems and the microbiome, we can develop more effective treatment strategies, improve patient outcomes, and promote a greater understanding of the human body’s remarkable capabilities.
Google News | Telegram