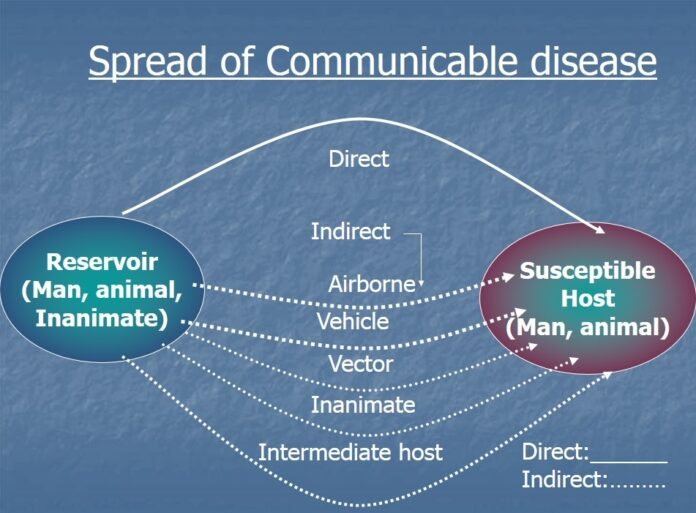
Communicable diseases have been a major challenge throughout human history, causing significant morbidity and mortality. From the bubonic plague to the Spanish flu and the current COVID-19 pandemic, infectious diseases have shaped human civilization, impacting everything from economics and politics to social norms and cultural practices. While significant progress has been made in controlling and preventing communicable diseases, they remain a significant threat to global health. In this article, we will discuss the present and future challenges of communicable diseases and explore potential solutions to address these challenges.
The Present Challenge of Communicable Diseases
The current COVID-19 pandemic has brought to the forefront the present challenge of communicable diseases. The pandemic has impacted every aspect of life, causing widespread illness, death, and economic disruption. As of March 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) has reported over 423 million confirmed cases of COVID-19 and over 5.8 million deaths worldwide.
The pandemic has highlighted several challenges associated with communicable diseases, including the rapid spread of infectious agents, the potential for asymptomatic transmission, and the limited effectiveness of current control measures. The emergence of new variants of the virus that are more transmissible or more resistant to existing vaccines and therapies has further complicated the control of the pandemic.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also exposed the global health disparities and inequalities that exist. Low- and middle-income countries have been disproportionately affected by the pandemic, with limited access to testing, treatment, and vaccines. The pandemic has highlighted the need for more equitable distribution of resources and the importance of building resilient health systems.
The Future Challenge of Communicable Diseases
While significant progress has been made in controlling and preventing communicable diseases, there are several challenges that we will face in the future. One of the biggest challenges is the emergence of new infectious agents. The rapid pace of globalization, travel, and urbanization has increased the risk of zoonotic diseases, which can jump from animals to humans. Climate change and deforestation can also contribute to the emergence and spread of infectious diseases by altering ecosystems and increasing contact between wildlife and humans.
Another challenge is the potential for antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Overuse and misuse of antibiotics have led to the development of bacteria and other pathogens that are resistant to existing drugs. This can make infections more difficult to treat and increase the risk of mortality. According to the WHO, AMR is one of the top 10 global public health threats facing humanity.
In addition to these challenges, communicable diseases will continue to impact global health disparities and inequalities. Low- and middle-income countries are more likely to experience outbreaks of communicable diseases due to limited access to healthcare, sanitation, and hygiene. This can lead to higher rates of morbidity and mortality and can exacerbate existing social and economic inequalities.
Solutions to Address Communicable Diseases
To address the present and future challenges of communicable diseases, several solutions are necessary. One of the most important solutions is strengthening health systems. This includes investing in healthcare infrastructure, training healthcare workers, and improving access to essential medicines, vaccines, and diagnostics. Strengthening health systems can improve the capacity to detect and respond to outbreaks, provide timely and effective treatment, and prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
Another solution is investing in research and development. This includes developing new drugs, vaccines, and diagnostic tools to prevent and treat communicable diseases. Additionally, research is needed to understand the drivers of the emergence and spread of infectious diseases and to develop effective strategies to mitigate these risks.
Another solution is promoting global health security. This includes improving surveillance and monitoring systems, building partnerships and collaborations between countries, and improving preparedness and response to outbreaks. Global health security can help prevent the emergence and spread of infectious diseases and mitigate their impact when they occur.
Finally, addressing communicable diseases requires addressing social determinants of health. This includes improving access to clean water and sanitation, promoting education and awareness about communicable diseases, and addressing economic and social inequalities. Addressing social determinants of health can help prevent the emergence and spread of communicable diseases by improving living conditions and reducing the risk of exposure to infectious agents.
Conclusion
Communicable diseases remain a significant challenge to global health, with the potential to cause significant morbidity and mortality. While significant progress has been made in controlling and preventing communicable diseases, there are still present and future challenges that need to be addressed. This includes strengthening health systems, investing in research and development, promoting global health security, and addressing social determinants of health.
Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort between governments, healthcare organizations, researchers, and individuals. By working together, we can mitigate the impact of communicable diseases and promote global health and wellbeing. As we continue to face the current COVID-19 pandemic and prepare for future outbreaks, it is essential that we prioritize the prevention and control of communicable diseases as a global health priority.
Google News | Telegram